Calculate BMI Using NHS BMI Healthy Weight Calculator
The NHS BMI Calculator is a BMI caculator that helps individuals calculate their Body Mass Index (BMI) and determine whether their weight falls within a healthy range. BMI is a widely used measure of body fat based on a person’s height and weight, and is often used as an indicator of overall health.
Using the NHS BMI Calculator is simple and straightforward. To calculate your BMI, all you need to do is enter your height and weight into the calculator, and click on the “Calculate BMI” button. The calculator will then provide you with a BMI score, along with a message that indicates whether you are underweight, a healthy weight, overweight, or obese.
It’s important to note that while BMI Calculator NHS can be a useful tool for assessing weight status, it is not a perfect measure of health. For example, it doesn’t take into account factors such as muscle mass or body composition. Therefore, it’s important to use BMI in conjunction with other measures such as waist circumference, body fat percentage, and overall health assessments.
If you are concerned about your BMI score or weight status, it’s a good idea to consult with a healthcare professional. They can provide you with personalized recommendations for achieving and maintaining a healthy weight, as well as refer you to resources and support services available through the NHS.
BMI Weight Calculator
NHS Weight Chart
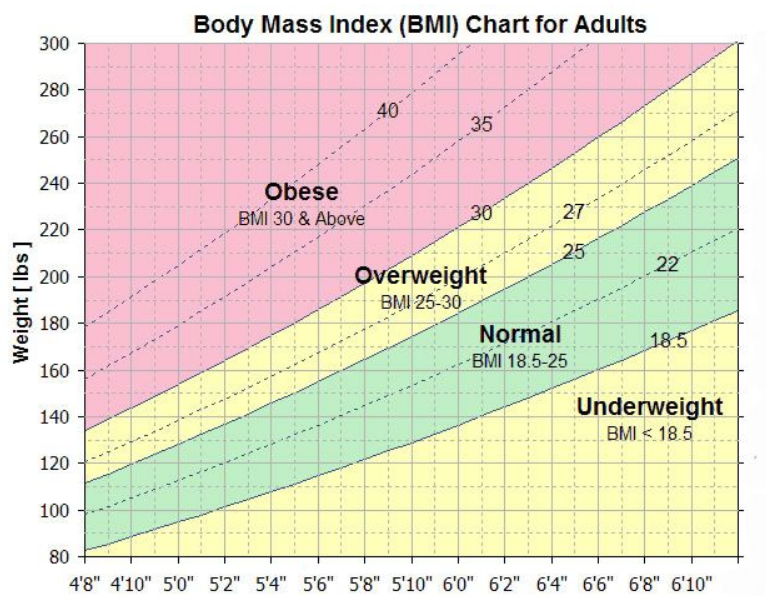
Understanding BMI and Its Importance for Health
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a widely used measure of body fat that is based on a person’s weight and height. BMI is a useful tool for assessing weight status and determining whether an individual is underweight, a healthy weight, overweight, or obese. Understanding BMI and its importance for health can help individuals make informed decisions about their weight and overall health.
BMI is calculated by dividing a person’s weight in kilograms by their height in meters squared. A BMI score of less than 18.5 is considered underweight, a score between 18.5 and 24.9 is considered a healthy weight, a score between 25 and 29.9 is considered overweight, and a score of 30 or higher is considered obese. These categories are based on the relationship between BMI and the risk of chronic diseases such as diabetes, heart disease, and certain types of cancer.
Maintaining a healthy BMI is important for overall health and can reduce the risk of chronic conditions. For example, research has shown that a higher BMI is associated with an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, and heart disease. Conversely, maintaining a healthy BMI can reduce the risk of these conditions and improve overall health outcomes.
However, it’s important to note that BMI is not a perfect measure of health. It doesn’t take into account factors such as muscle mass or body composition, which can be important indicators of overall health. Therefore, BMI should be used in conjunction with other measures such as waist circumference, body fat percentage, and overall health assessments.
Weight Understanding
Underweight:
If your BMI falls in the underweight category, it could indicate that you are not consuming sufficient food or that you might be experiencing an illness. It is crucial to consult a general practitioner if you are underweight. They can assist you in identifying the root cause and provide advice on how to reach a healthy weight.
Healthy weight:
If your BMI falls into the healthy weight range, well done! You are making progress in maintaining a healthy weight. To continue your good work, have a look at the food and diet and fitness sections for advice on sustaining a healthy weight.
Weight Understanding
Overweight:
If your BMI falls into the overweight category, it is crucial to take action to reduce your weight. The optimal approach is a combination of diet and exercise. The NHS BMI calculator can provide you with a customized calorie allowance to assist you in safely reaching a healthy weight.
Obese:
If your BMI falls into the obese category, it’s essential to take measures to reduce your weight. The best approach is a combination of diet and exercise, and in some instances, medication. Seeking guidance and advice from a GP is important in such cases.
How to Measure Your Height and Weight Accurately for BMI Calculation?
To calculate your BMI using the NHS BMI calculator, you need to have accurate measurements of your height and weight. Here’s how to measure your height and weight accurately:
- Measuring Your Height:
Stand against a wall, barefoot and with your back straight, and follow these steps:
- Use a measuring tape or ruler to measure your height in centimeters (cm).
- Make sure the measuring tape is flat against the wall and level with the floor.
- Stand with your heels, buttocks, shoulders, and head touching the wall.
- Look straight ahead and take a deep breath in.
- Make sure the measurement is accurate to the nearest centimeter.
- Measuring Your Weight:
To measure your weight accurately, follow these steps:
- Use a reliable weighing scale that is placed on a flat and even surface.
- Wear lightweight clothing and remove your shoes before weighing yourself.
- Stand on the scale with your feet slightly apart and your arms at your sides.
- Look straight ahead and keep your body still.
- Read the measurement on the scale once it has stabilized.
After obtaining these measurements, input them into the NHS BMI calculator to calculate your BMI. If you fall into the overweight or obese categories, consider consulting a GP for further guidance and support. By maintaining a healthy weight, you can reduce the risk of chronic health conditions and improve overall health outcomes.
Interpreting Your BMI Score: What It Means for Your Health
Interpreting your BMI score is an essential step in assessing your overall health and wellbeing. Using the NHS BMI calculator or BMI NHS calculator, you can calculate your BMI score, which is a measure of your body fat based on your weight and height.
Your BMI score falls into one of four categories:
Underweight: A BMI score under 18.5 indicates that you may be underweight and at risk of malnutrition and other health problems.
Healthy weight: A BMI score between 18.5 and 24.9 indicates that you are at a healthy weight range for your height.
Overweight: A BMI score between 25 and 29.9 indicates that you may be overweight, and there is a risk of developing health problems such as diabetes, high blood pressure, and heart disease.
Obese: A BMI score of 30 or higher indicates that you may be obese and at a higher risk of developing serious health conditions such as cancer, sleep apnea, and arthritis.
It’s important to note that while BMI is a useful tool for assessing your weight status, it does not take into account factors such as muscle mass and body composition. As such, it’s crucial to consider other factors such as waist circumference and overall health when interpreting your BMI score.
If your BMI score falls in the overweight or obese categories, it’s essential to take steps to reduce your weight through a combination of diet and exercise. Seeking guidance and support from a healthcare professional, such as a GP, can also be helpful in managing your weight and reducing the risk of developing health problems.
Overall, interpreting your BMI score using the NHS BMI calculator or BMI NHS calculator can provide valuable insights into your weight status and overall health. By maintaining a healthy weight, you can improve your health outcomes and reduce the risk of chronic health conditions.
Limitations and Criticisms of BMI as a Health Measure
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a widely used measure of body fat that uses a person’s height and weight to calculate their BMI score. However, while BMI is a useful tool for assessing weight status, it has several limitations and criticisms as a health measure.
Here are some of the limitations and criticisms of BMI:
It doesn’t differentiate between fat and muscle mass: BMI doesn’t take into account factors such as muscle mass, which can lead to inaccurate results, particularly for athletes and bodybuilders.
It doesn’t account for body shape: BMI doesn’t differentiate between different body shapes, such as apple-shaped or pear-shaped, which can affect health outcomes.
It doesn’t account for age and gender differences: BMI doesn’t account for age and gender differences, which can affect the interpretation of BMI scores for older adults, women, and children.
It doesn’t consider overall health: BMI doesn’t consider other factors that can affect health, such as diet, exercise, genetics, and lifestyle habits.
It may not be suitable for certain ethnic groups: Some studies suggest that BMI may not be a suitable measure of body fat for certain ethnic groups, such as Asians and Pacific Islanders.
Despite these limitations and criticisms, BMI remains a useful tool for assessing weight status in the general population. It’s essential to interpret BMI scores in conjunction with other measures of health, such as waist circumference, blood pressure, and overall health status.
In summary, while BMI has limitations and criticisms as a health measure, it remains a useful tool for assessing weight status in the general population. Understanding its limitations and considering other measures of health can help improve the accuracy of BMI as a health measure.
The Link Between BMI and Chronic Health Conditions
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a measure of body fat based on a person’s height and weight. Studies have shown that high BMI scores are strongly associated with chronic health conditions, such as type 2 diabetes, heart disease, stroke, high blood pressure, and certain types of cancer.
Here are some of the ways in which BMI is linked to chronic health conditions:
Type 2 diabetes: High BMI scores are strongly associated with insulin resistance and an increased risk of type 2 diabetes. This is because excess body fat can cause inflammation and interfere with the body’s ability to use insulin effectively.
Heart disease and stroke: High BMI scores are associated with an increased risk of heart disease and stroke. This is because excess body fat can lead to high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and other risk factors for heart disease and stroke.
High blood pressure: High BMI scores are associated with an increased risk of high blood pressure. This is because excess body fat can cause inflammation and interfere with the body’s ability to regulate blood pressure.
Certain types of cancer: High BMI scores are associated with an increased risk of certain types of cancer, including breast, colon, and prostate cancer. This is because excess body fat can cause inflammation and interfere with the body’s ability to regulate hormones that can contribute to cancer growth.
Overall, high BMI scores are strongly linked to chronic health conditions that can significantly impact a person’s quality of life and longevity. Maintaining a healthy BMI through a balanced diet, regular exercise, and other healthy lifestyle habits can help reduce the risk of chronic health conditions and improve overall health outcomes.
BMI Calculator NHS Choices
The NHS offers a BMI Calculator as a tool to determine whether an individual’s body mass index (BMI) falls within a healthy range. This calculator takes into account a person’s height and weight to classify their BMI as underweight, healthy weight, overweight, or obese.
The calculator also provides information on the potential health risks associated with being overweight or obese, along with advice on how to achieve and maintain a healthy weight. It even considers age and gender, as well as height and weight for children and young people aged 2 to 18.
Using the calculator is simple – just enter your weight and height, and it will give you your BMI along with information on your weight status and the potential health risks. Additionally, the calculator offers the option to measure your waist size, which is a good way to check whether you’re carrying too much fat around your stomach. Carrying too much fat in this area can increase your risk of heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and stroke.
However, it’s important to note that BMI is not always an accurate measure of health. Factors such as muscle mass, age, and overall fitness should also be taken into account when assessing weight. Therefore, if you have concerns about your weight or body fat percentage, it’s recommended to consult a GP or a dietitian.
NHS BMI Healthy Weight Calculator
The NHS BMI Healthy Weight Calculator is a helpful tool offered by the UK’s National Health Service (NHS) that enables individuals to determine their ideal body weight and make informed decisions about their health. This resource takes into account various physiological measurements such as age, gender, height, and weight for children aged 2-18, as well as the potential risks associated with being underweight or overweight. By utilizing this information, the calculator provides an individual’s precise BMI reading and advice on achieving optimal wellness through proper nutrition habits.
Measuring your BMI is a crucial component of maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Our user-friendly calculator provides you with essential information, not only on weight but also on waist size. This is particularly important to avoid potential health risks associated with carrying excess fat around your stomach, such as heart disease and type 2 diabetes. However, it’s worth noting that other factors, such as muscle mass, age, and overall fitness, should also be considered when assessing one’s weight. If you have any further concerns in this regard, it is recommended to consult with a GP or a dietitian.
Understanding Your Body Mass Index (BMI) with the NHS BMI UK Calculator
Maintaining a healthy weight is essential for overall health and wellbeing. The body mass index (BMI) is a tool used by healthcare professionals to assess whether someone is at a healthy weight or not. The National Health Service (NHS) in the UK provides an easy-to-use BMI calculator to help individuals determine their BMI and understand its implications for their health.
What is BMI?
BMI is a measurement of body fat based on a person’s height and weight. It provides a general guideline to assess whether someone is underweight, within a healthy weight range, overweight, or obese. BMI is not a direct measure of body fat, but it is a good indicator for most people.
How to use the NHS UK BMI Calculator?
The NHS UK BMI calculator is an easy-to-use tool that takes into account age, gender, height, and weight to determine an individual’s BMI. To use the calculator, simply visit the NHS UK BMI Calculator website and input your height and weight. The calculator will then provide you with your BMI score and tell you whether you fall under the underweight, healthy weight, overweight, or obese categories.
What does your BMI score mean?
The BMI score can help you understand your risk for developing certain health conditions. Generally, a BMI score between 18.5 and 24.9 is considered healthy, while a score below 18.5 indicates being underweight and a score of 25 or higher indicates being overweight or obese.
However, it is important to note that BMI is not always an accurate measure of health. For example, someone with a lot of muscle mass may have a high BMI score but still be healthy. On the other hand, someone with a low BMI score may have a high percentage of body fat and be at risk for health problems.
What are the health implications of BMI?
Being overweight or obese can increase the risk of developing a variety of health problems, such as heart disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, and some cancers. On the other hand, being underweight can also be associated with health problems such as malnutrition, weakened immune system, and fertility issues.
It’s important to understand that BMI is just one factor in assessing overall health. Other factors such as diet, exercise, genetics, and lifestyle habits also play a role. It’s always recommended to consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice and guidance.